How to Disavow Toxic Backlinks
- rei-wakayama
- 5 days ago
- 3 min read
Updated: Jan 6, 2026
Spamdexing, or search engine spam, is the bad practice of using black-hat SEO tactics such as keyword stuffing or hidden texts and links, to manipulate search engine results. Obviously, spamdexing violates Google’s webmaster guidelines, and if you are caught, your site may face a Google penalty and deindexing. Keyword stuffing may have worked 20 years ago, but now in 2026, search engines like Google are continually improving their algorithms to identify spamdexing.
How to Prevent Spamdexing on Your Website
To prevent spamdexing, focus on implementing technical SEO best practices, maintain robust website security, and monitor your backlinks. As I have previously published blog posts on how to do a technical SEO audit and enhance website security, this post will focus on backlinks.
What is a Toxic Backlink?
Backlinks are generally a positive factor in SEO. If a user finds your website's content informative, they might link to it from their own site. That backlink is a vote of confidence in your content. However, toxic backlinks display signs of black hat tactics - low domain authority, mirrored pages, duplicate content, spammy websites, and low visible text to html ratio.
SEOs should monitor for toxic backlinks by setting up Google Alerts and using the link report in Google Search Console or a backlink analysis tool. SEMrush, or Moz subscriptions include a free backlink checker to help you work efficiently and spot toxic backlinks quickly.
Even if you are sticking to white hat SEO, you may receive toxic backlinks and get penalized for them, regardless of whether or not you were knowingly complicit.
Google's Algorithm for Spam Detection
Unlike some other SEO factors, Google is very clear about their position and approach to toxic backlinks. Having too many toxic backlinks pointing to your website can weaken your website's SEO or even get you penalized from search engines.
Seasoned SEOs may remember Google's Penguin, an algorithm that catches toxic backlinks, released in 2012. Penguin as a standalone algorithm has since been sunset replaced by SpamBrain, Google’s current spam-detection algorithm designed to find and remove low-quality websites from the SERPs. An algorithmic penalty from SpamBrain can result in a significant drop in rankings and organic traffic, or even complete de-indexing of your site.
The webspam team at Google also reviews link profiles manually. Manual review could be triggered for several reasons, including but not limited to:
Spam report from a competitor
Algorithmic penalty triggered a manual review
Your business is in a competitive niche that Google actively monitors
Google usually does not notify you directly for algorithmic penalties. For manual penalties, you'd receive a notification in Google Search Console.
How to Disavow Toxic Backlinks
The disavow links tool is a feature in Google Search Console that lets website owners tell Goole to ignore toxic backlinks pointing to their site, preventing them for negatively impacting search rankings. You can disavow a specific link, subdomain, or entire domain.
# Two pages to disavow
http://spam.example.com/stuff/comments.html
http://spam.example.com/stuff/paid-links.html
# One domain to disavow
domain:shadyseo.comDespite some rumors that Google will follow Bing in completely removing the disavow tool, it is still live as of January 2026.
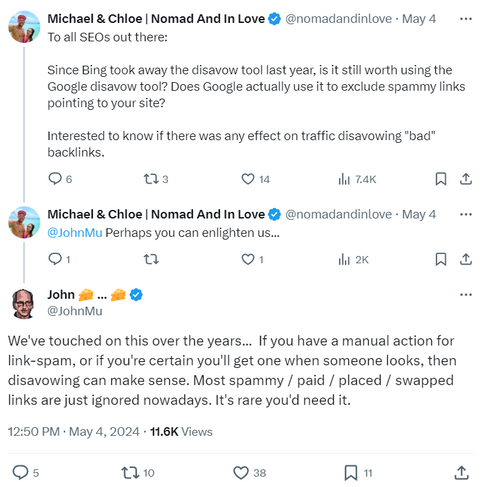
John Mueller has confirmed that in most cases, it's not necessary to use the disavow tool. As described in the previous section, Google is already pretty good at ignoring link spam, and many SEOs have reported no significant change from using the disavow tool preventatively. Cyrus Shepard even ran an experiment where he disavowed every link to his site, and nothing happened.
However, if Google notifies you about a manual link-based penalty, you can try to recover by disavowing the toxic backlinks. You can also file a spam report with Google, providing details of the attack.
Note that when you disavow links, it means that you are requesting Google to disregard the toxic links to your domain. Similar to rel=canonical, it's a suggestion rather than a directive. Although disavows are accepted in most cases, Google is not obligated to honor them.